<aside>

CVXPY 提供凸性检测,原理是 Disciplined Convex Programming ,网页入口:
https://dcp.stanford.edu/home | DCP analyzer:
将函数用cvxpy自带的 Functions 表示,会返回凸性分析结果。
将函数用cvxpy自带的 Functions 表示,会返回凸性分析结果。
[ ] 凸函数与凸集什么关系?为什么说凸集的定义更普适? </aside>
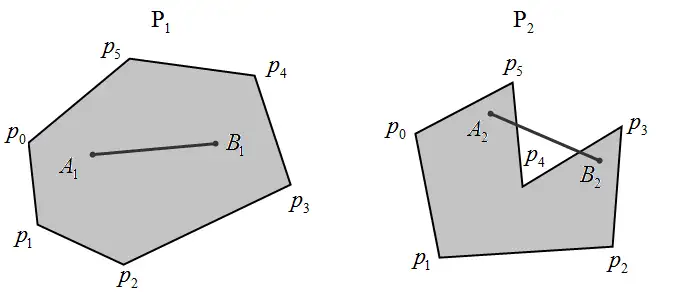
A set is convex: $x\in S,y\in S$→ segment $xy\subset S$.
segment $xy:\alpha x+\beta y,\alpha,\beta\ge0,\alpha+\beta =1$. to Convex Combination to barycentric coordinates.
凸集定义为存在加法运算和对应标量空间的集合的子集,满足集合中任意元素的凸组合仍在集合内。
$$ \boxed{ \alpha x+\beta y\in \Omega}\\x,y\in \Omega,\alpha +\beta=1,\alpha,\beta \in \R $$
凸组合是两变量的线性组合,其线性因子和为1。
锥组合类似,线性因子非负
Python库:SciPy.spatial.ConvexHull
<aside>
顶点定义法:有限点集中有限个极点Exteme Point构成的凸对象Convex Object
【极点】
极点是不能由凸多胞体内其他点的凸组合Convex Combination表出的点
$$ a_1x_1+...+a_kx_k,a_i\ge0,a_1+...+a_k=1. $$
一条线段:端点的所有凸组合
半空间Half Space交定义法:一个凸多胞体表示成有限个半空间相交的封闭Closed空间(有边界)
超平面,把$R^n$空间分成两半的平面
$$ \Gamma:a_1x_1+a_2x_2+...+a_nx_n=b.\\ Half\_Space:a_1x_x+a_2x_2+...+a_nx_n\le b. $$
面facet:凸多胞体$P$的面$F:P \cap \{x:a\cdot x = b\}$
岭Ridge:一个面的边界,两个面的邻接Adjacency部分
欧拉公式:三维空间$V-E+F=2$,多面体的顶点数,边数,面数
</aside>
Some formal definitions and approaches.
Convex Hull 凸包 of a set of $S$ is the set of all convex combinations of points of $S$. $conv S,\mathcal{H} (S)$.
all convex combinations of S → of $\le d+1$ of $S$ by Caratheodory’s Theorem, Lay 1982.
is the intersection of all convex sets that contains $S$.
is the intersection of all halfspaces that contains $S$ & closed.
convex hell of a finite set of points $S$ is the smallest convex polygon $P$ that encloses $S$.[subset nesting]
is the enclosed convex polygon $P$ with smalest area.
is the enclosed convex polygon $P$ with smalest perimeter.
is the union of all the triangles determined by points in $S$
凸函数的上图可通过透视法扩展为凸锥(包),凸优化 Convex Optimization 进而规约为锥规划 Conic Optimization
closed conic hull of its epigraph (conic extensions)
凸函数的上图可以用锥闭包(凸包)表示,只需增加一个透视 perspective 维度$(x,t\ge f(x))$ → $(x,s,t),s>0$
$$ cl\{(t,s,x)\in \mathbb R^{1\times 1\times n}\mid \frac ts\ge f(\frac xs),s\ge 0\} $$
单纯的凸集不能满足cone $kv\in \Omega,\forall v\in \Omega$

注意,“透视源”不一定是点,可以是线、面,只要作为极限存在并以边界点囊括入闭包即可。
Rockafellar, R.T.: Level sets and continuity of conjugate convex functions. Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 123(1), 46–63 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9947-1966-0192318-X
如指数锥常表示为第三象限和透视锥的并集。
指数函数生成指数锥
$$ \mathcal K_{\exp}\equiv cl([\mathcal K_{\exp}]{++}) =[\mathcal K{\exp}]{++} \cup[\mathcal K{\exp}]_{0} $$
其中$[\mathcal K_{\exp}]_{++}$是指数函数符合透视的集合(perspective interior)
$$ [\mathcal K_{\exp}]_{++} =\big\{ (t,s,x)\in \mathbb R^{1\times 1\times n}\mid \frac ts\ge \exp(\frac xs),s\ge 0 \big\} $$
作为闭包,需要考虑并包括边界点。这里就是取$s\to 0$后只有极限定义的点集(指数函数被无穷缩小,取极限后上图为第四象限全体, perspective boundary)
$$ [\mathcal K_{\exp}]_{0} =\big\{ s=0,t\ge 0,r\le 0 \big\} $$
<aside>
Friberg - 2023 - Projection onto the exponential cone a univariate root-finding problem.pdf
指数锥优势
expressive abilities
指数函数上图,对数函数下图,exponentials指数多项式,logarithms,entropy funxtions熵,product logarithms, soft-max, soft-plus
numerically stable 3-self-concordant barrier functions
兼容对偶、facial reduction、内点特性
非symmetric cone,仍然能够快速收敛 </aside>
一阶优化算法中的投影法 3. 指数锥的投影问题